Capital budgeting is key for strategic business finance planning as it allows firms to decide on long-term investments using data. The capital budgeting process is a structured approach to evaluating and selecting long-term investments that align with a company’s strategic goals. This process starts from coming up with concepts from different parts within the organization such as the senior management or departmental heads among others. These suggestions go through a thorough scrutiny where managers predict cash flows, study costs and revenues so as to ascertain their workability.
Discounted Cash Flow Analysis
This involves the process of analyzing and assessing the actual results over the estimated outcomes. This step helps the management identify the flaws and eliminate them for future proposals. Using the Discounted Payback period method, we can check if the project selection is worthwhile or not. Let us go through some examples to understand the capital budgeting techniques. Companies often communicate between departments and rely on financial leadership to help prepare annual or long-term budgets. These budgets are often operational, outlining how the company’s revenue and expenses will shape up over the subsequent 12 months.
Evaluate and Compare Projects
- Managers face challenges of making appropriate capital decisions pertaining to long-term investments.
- It’s especially useful for businesses with long-term projects where reinvestment at the IRR might not be realistic.
- Taking up investments in a business can be motivated by a number of reasons.
- In this case, if you add up the yearly inflows, you can easily identify in which year the investment and returns would close.
- External factors like economic conditions and technological advancements can significantly impact the success of long-term investments.
- These investments could involve purchasing new equipment, expanding facilities, launching new product lines, or acquiring assets that will generate future cash flows over time.
- Also, payback analysis doesn’t typically include any cash flows near the end of the project’s life.
Pazy offers real-time insights into your financial data, providing an up-to-date view of capital budgeting performance. This visibility allows businesses to monitor cash flows and make quick adjustments as needed. Pazy automates key financial processes in capital budgeting, reducing manual errors and saving time. This automation ensures efficient analysis and seamless decision-making across investment projects. PI is the ratio of the present value of future cash inflows can law firms measure ambition without billable hours to the initial investment. Even if this is achieved, there are other fluctuations like the varying interest rates that could hamper future cash flows.
Conducting a SWOT analysis
The process of assessing the quality and profitability of a potential investment based on its expected cash flows. Therefore, the capital rationing method involves a complex decision-making process that considers multiple factors such as project profitability, risk, and liquidity. The decision-making process often involves using quantitative and qualitative criteria to evaluate each project’s potential impact on the firm’s financial performance.
- Pazy provides in-depth market analysis and financial risk assessment to help address key factors in capital budgeting.
- So far in the article, we have observed how measurability and accountability are two primary aspects that achieve the center stage through capital budgeting.
- It refers to the time taken by a proposed project to generate enough income to cover the initial investment.
- So, the initial investment requirement for project B is met in the 4th year.
- Quantitative analysis includes using financial figures to analyze the scenarios or alternatives of a given project or investment that is being pursued.
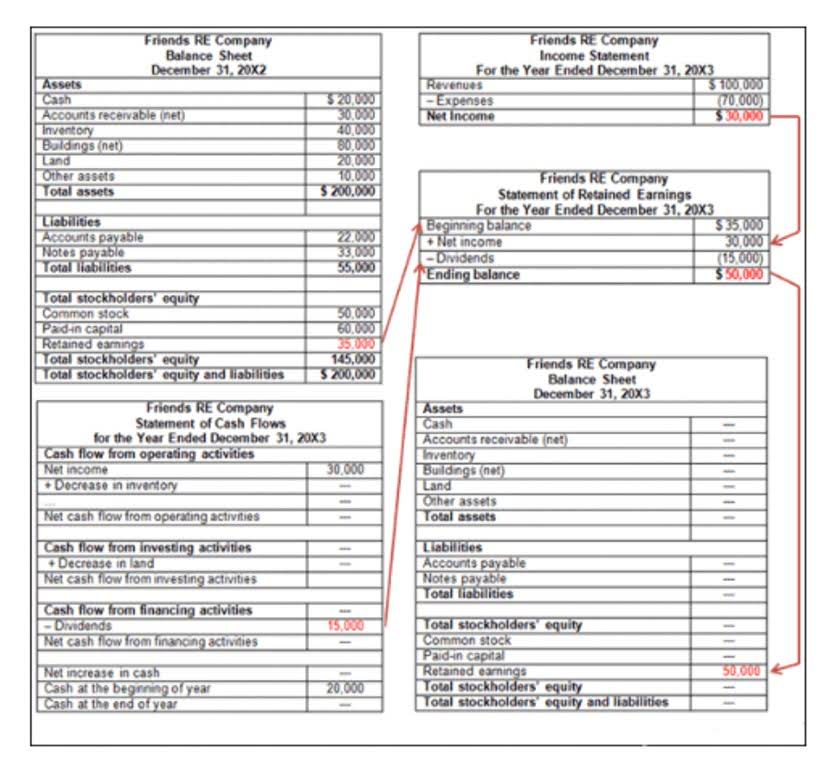
Capital Budgeting refers to the planning process which is used for decision making of the long term investment. It helps in deciding whether the projects are fruitful for the business and will provide the required returns in the future years. Capital budgets are internal documents used for planning, just like all other budgets. These reports aren’t required to be disclosed to the public and they’re mainly used to support management’s strategic decision making.
So That Happened: Gum in the News and More Grid Investments
By following a systematic series of steps, you can make better, data-driven decisions about where to allocate your resources. The process ensures that every investment is carefully considered, evaluated, and aligned with your business objectives. When applying the time value of money to capital budgeting, it’s essential to recognize that the value of future cash flows is not equal to their nominal amount. To account for this, discounting is used to adjust future cash flows to their present value.
Some companies want to track when the company breaks even or has paid for itself. Others are more interested in the timing of when a capital endeavor earns a certain amount of profit. Capital budgeting relies on many of the same fundamental pay virtually any bill with credit cards practices as any other form of budgeting but it has several unique challenges. They don’t incur revenue during the project and must be funded from an outside source such as revenue from a different department.
Through capex budgeting, management can chart a course for future growth spanning over a decade. The payback period is calculated by dividing the initial investment by the annual cash inflows. It indicates how long it will take to recover the initial investment from a project’s cash returns.
What do most capital budgeting methods primarily use?
Every business has diverse requirements and therefore, the approval over a project comes based on the objectives of the organization. It mainly consists of selecting all criteria necessary for judging the need for a proposal. Assuming the values given in the table, we shall calculate the profitability index for a discount rate of 10%.
While unexpected events can disrupt short-term cash flow, the timeframes involved are shorter, allowing for quicker adjustments. All in all, the follow-up system for all the invoices can be passed on to the system of Deskera Books and it will look into it for you. You can have access to Deskera’s ready-made Profit and Loss Statement, Balance Sheet, and other financial reports in an instant. Such cloud systems substantially improve cash flow for your business directly as well as indirectly.
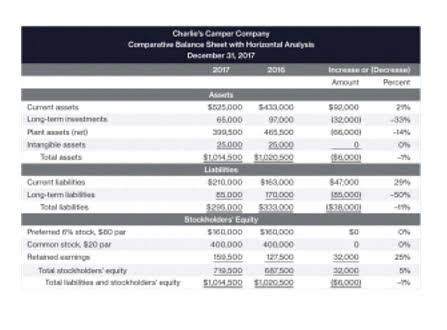
When all companies are included in the analysis, depreciation was 5% of COGS. Animal Feedstocks has the lowest, at 3%, followed by Industrial Machinery, Animal Health and Steel, at 4%, then Food and Beverage, Automotive, and Household Goods, at 5%. The downside of Monte Carlo simulations is that they require significant data, expertise, and computational resources to execute. The results are only as good as the underlying assumptions and models used, and there’s still uncertainty in choosing the right probability distributions for the inputs.
Tools for capital budgeting
A higher discount rate accounts for higher risk, while a lower discount rate reflects lower risk. Sensitivity analysis is one of the simplest and most widely used techniques for evaluating risk in capital budgeting. It involves testing how sensitive a project’s outcomes are to changes in key variables. For example, you might look at how changes in sales projections, production costs, or discount rates impact the Net Present Value (NPV) or Internal Rate of Return (IRR) of an investment. The capital budgeting process is a structured approach to evaluating and selecting investment projects that will benefit your company in the long term.
Benefits of strategic CAPEX planning
Capital budgeting is the process through which a business evaluates and decides on long-term investments or projects that require significant capital expenditures. These investments could involve purchasing new equipment, expanding facilities, launching new product lines, or acquiring assets that will generate future cash flows over time. The goal of capital budgeting is to determine whether these investments will provide valuing bonds payable sufficient returns to justify the initial costs.
Opting for cloud-based systems helps increase productivity and cut budgeting process timelines. Cincinnati Bell, a telecommunications company, reported improved communication and visibility across 100 users after automating their FP&A processes with Limelight, a cloud-based, Excel-free platform. This helped them achieve 20% more productivity and 75% faster reporting cycles. Cloud-based tools enable teams across different locations to collaborate on CAPEX planning in real-time. These solutions are particularly beneficial for companies operating in multiple geographies or industries with complex approval workflows. For instance, a tech startup might prioritize projects that enhance cybersecurity over those that improve office aesthetics, given the higher strategic value of security investments.
Setting long-term goals and objectives
By quantifying risks, firms can develop strategies to mitigate potential adverse effects. It is a simple technique that determines if an enhanced value of a project justifies the required investment. The primary reason to implement capital budgeting is to achieve forecasting revenue a project may possibly generate. All the upfront costs or the future revenue are all only estimates at this point. An overestimation or an underestimation could ultimately be detrimental to the performance of the business.